ENCLOSURE TYPE FOR ELECTRIC MOTOR SPECIFICATIONS
How do they specify the enclosure of an Electric Motor?
When the degree of protection is specified by only one numeral, the omitted numeral is replaced by the letter X. For example, IPX5 or IP2X.
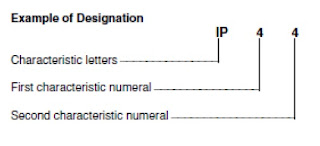
The first Characteristic Numeral indicates the degree of protection provided by the enclosure with respect to persons and also to the parts of the machine inside the enclosure.
The Second Characteristic Numeral indicates the degree of protection provided by the enclosure with respect to harmful effect due to ingress of water.
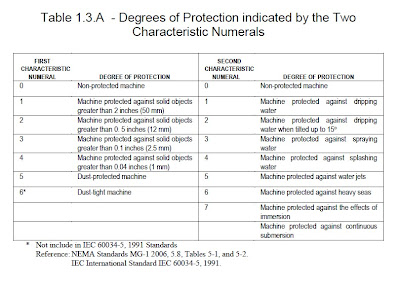
The two characteristic numerals signify conformity with the conditions indicated in Table 1.3.A. – Degrees of Protection Indicated by the Two Characteristic Numerals.
How do they specify the enclosure of an Electric Motor?
The enclosure of the motor must protect the windings, bearings, and other mechanical parts from moisture, chemicals, mechanical damage and abrasion from grit. NEMA standards MG1-1.25 through 1.27 define more than 20 types of enclosures under the categories of open machines, totally enclosed machines, and machines with encapsulated or sealed windings. The most commonly used motor enclosures are open dripproof, totally enclosed fan cooled and explosionproof.
The Standards for IP Codes apply to the classification of degrees of protection provided by enclosure for all rotating machines. The designation used for the degree of protection consists of the letter IP (International Protection) followed by two characteristic numerals.
The first Characteristic Numeral indicates the degree of protection provided by the enclosure with respect to persons and also to the parts of the machine inside the enclosure.
The Second Characteristic Numeral indicates the degree of protection provided by the enclosure with respect to harmful effect due to ingress of water.
The two characteristic numerals signify conformity with the conditions indicated in Table 1.3.A. – Degrees of Protection Indicated by the Two Characteristic Numerals.
VARIOUS MOTOR ENCLOSURES IMAGES
Open Dripproof.
The open dripproof motor (ODP) has a free exchange of air with the ambient. Drops of liquid or solid particles do not interfere with the operation at any angle from 0 to 15degrees downward from the vertical. The openings are intake and exhaust ports to accommodate interchange of air. The open dripproof motor is designed for indoor use where the air is fairly clean and where there is little danger of splashing liquid.
Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled (TEFC).
This type of enclosure prevents the free exchange of air between the inside and outside of the frame, but does not make the frame completely airtight. A fan is attached to the shaft and pushes air over the frame during its operation to help in the cooling process. The ribbed frame is designed to increase the surface area for cooling purposes. There is also a totally enclosed non-ventilated (TENV) design which does not use a fan, but is used in situations where air is being blown over the motor shell for cooling, such as in a propeller fan application.
Explosionproof
The explosionproof motor is a totally enclosed machine and is designed to withstand an explosion of specified gas or vapor inside the motor casing and prevent the ignition outside the motor by sparks, flashing or explosion. These motors are designed for specific hazardous purposes, such as atmospheres containing gases or hazardous dusts. For safe operation, the maximum motor operating temperature must be below the
ignition temperature of surrounding gases or vapors. Explosionproof motors are designed, manufactured and tested under the rigid requirements of the Underwriters Laboratories. Hazardous location motor applications are classified by the type of hazardous environment present, the characteristics of the specific material creating the hazard, the probability of exposure to the environment, and the maximum temperature level that is considered safe for the substance creating the hazard. The format used to define this information is a class, group, division and temperature code structure.
source: 2010 IIEE Technical Manual
The open dripproof motor (ODP) has a free exchange of air with the ambient. Drops of liquid or solid particles do not interfere with the operation at any angle from 0 to 15degrees downward from the vertical. The openings are intake and exhaust ports to accommodate interchange of air. The open dripproof motor is designed for indoor use where the air is fairly clean and where there is little danger of splashing liquid.
Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled (TEFC).
This type of enclosure prevents the free exchange of air between the inside and outside of the frame, but does not make the frame completely airtight. A fan is attached to the shaft and pushes air over the frame during its operation to help in the cooling process. The ribbed frame is designed to increase the surface area for cooling purposes. There is also a totally enclosed non-ventilated (TENV) design which does not use a fan, but is used in situations where air is being blown over the motor shell for cooling, such as in a propeller fan application.
Explosionproof
The explosionproof motor is a totally enclosed machine and is designed to withstand an explosion of specified gas or vapor inside the motor casing and prevent the ignition outside the motor by sparks, flashing or explosion. These motors are designed for specific hazardous purposes, such as atmospheres containing gases or hazardous dusts. For safe operation, the maximum motor operating temperature must be below the
ignition temperature of surrounding gases or vapors. Explosionproof motors are designed, manufactured and tested under the rigid requirements of the Underwriters Laboratories. Hazardous location motor applications are classified by the type of hazardous environment present, the characteristics of the specific material creating the hazard, the probability of exposure to the environment, and the maximum temperature level that is considered safe for the substance creating the hazard. The format used to define this information is a class, group, division and temperature code structure.
source: 2010 IIEE Technical Manual



IT IS MUCH HELPFUL ARTICLE AND IMPROVE KNOWLEDGE TO SHARE WITH SOME STUDENTS , MANY THANKS TO THOSE WHO CONCERN
ReplyDelete