How to compute for the losses found in transformers?
We mention in the previous articles the different types of internel energy dissipation of transformers. Here we will be showing you some basic formulas used in computing for the said losses;
1. The Core Loss of the Transformer
where: V1 - voltage rating
Io - exciting current in amps
cos0 - cosine of the angle between wattful current and exciting current
Rc - resistance representing the core loss
Ic - wattful current in amps
2. Steinmetz Law: Hysteresis Loss
where: V - core volume
kh - hysteresis constant (depending on the materials)
Bm - maximum flux density
1.6 - steinmetz constant
where: f - frequency
Ph - hysteresis loss in watts
3. Eddy-current Loss
where: Pe - eddy-current loss in watts
p - resistivity of the ferromagnetic material in ohm-meter
t - thickness of the lamination in meters
f - frequency in hertz
Bm - maximum flux density in Tesla
V - core volume in cu.meter
4. Core Loss with hysteresis and eddy-current componets
where: Ph - hysteresis loss
Pe - eddy-current loss
5. Copper (winding) Loss
where: I1 - current referred to primary
Ro - equivalent resistance referred to primary
The maximum efficiency of a transformer is said to be achieve when the winding loss is equal to the core loss or;
and, the load current at maximum efficiency can be computed by this formula;
These are some of the formulas used in computing for different transformer parameters especiall with respect to the energy dissipated.
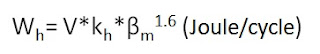
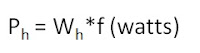


fremerdisp-pe Melvin Magee click
ReplyDeleteexrammidon