IMAGES OF CURRENT TRANSFORMERS INCLUDING TYPES AN DEFINITIONS
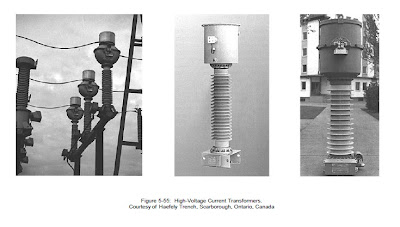
Images and Illustration of a typical current transformer for medium and high voltage level.
Bushing: A bushing-type current transformer is one that has a round core and a secondary winding insulated from and permanently assembled on the core but has no primary winding or insulation for a primary winding. This type of current transformer is for use with a fully insulated conductor as the primary winding.
Double-Secondary: A double-secondary current transformer is one that has secondary coils each on a separate magnetic circuit with both magnetic circuits excited by the same primary winding. Multiple-secondary (three or more) current transformers are also manufactured.
Window/Donut: A window- or donut-type current transformer is one that has a secondary winding insulated from and permanently assembled on the core, but has no primary winding as an integral part of the structure. Complete or partial insulation is provided for a primary winding in the window through which one or more turns of the line conductor can be threaded to provide the primary winding.
Wound: A wound-type current transformer is one that has a fixed primary winding mechanically encircling the core; it may have one or more primary turns. The primary and secondary windings are completely insulated and permanently assembled on the core as an integral structure.
Others: Other types are available in addition to those listed. Descriptions can be found in
manufacturers’ literature.
Images and Illustration of a typical current transformer for medium and high voltage level.
A current transformer is an instrument transformer intended to have its primary winding connected in series with the conductor carrying the current to be measured or controlled. The ratio of primary to secondary current is roughly inversely proportional to the ratio of primary to secondary turns and is usually arranged to produce either five amperes or one ampere (IEC Standard) in the full tap of the secondary winding when rated current is flowing in the primary.
Bar: A bar-type current transformer is one that has a fixed, insulated straight conductor in the form of a bar, rod, or tube that is a single primary turn passing through the magnetic circuit and that is assembled to the secondary, core, and winding.
Bushing: A bushing-type current transformer is one that has a round core and a secondary winding insulated from and permanently assembled on the core but has no primary winding or insulation for a primary winding. This type of current transformer is for use with a fully insulated conductor as the primary winding.
Double-Secondary: A double-secondary current transformer is one that has secondary coils each on a separate magnetic circuit with both magnetic circuits excited by the same primary winding. Multiple-secondary (three or more) current transformers are also manufactured.
Window/Donut: A window- or donut-type current transformer is one that has a secondary winding insulated from and permanently assembled on the core, but has no primary winding as an integral part of the structure. Complete or partial insulation is provided for a primary winding in the window through which one or more turns of the line conductor can be threaded to provide the primary winding.
Wound: A wound-type current transformer is one that has a fixed primary winding mechanically encircling the core; it may have one or more primary turns. The primary and secondary windings are completely insulated and permanently assembled on the core as an integral structure.
Others: Other types are available in addition to those listed. Descriptions can be found in
manufacturers’ literature.

Comments
Post a Comment