STANDARD REQUIREMENTS IN DEALING WITH VOLTAGE TRANSFORMERS
What is a Voltage Transformer with respect to C57.13?
Terms in which ratings shall be expressed
The ratings of a voltage transformer shall include:
a) Basic impulse insulation level in terms of full-wave test voltage
b) Rated primary voltage and ratio
c) Frequency (in Hertz)
d) Accuracy ratings
e) Thermal burden rating
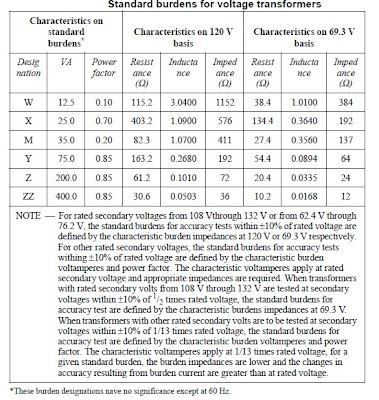
Standard burdens
Standard burdens for voltage transformers for rating purposes are shown in table below.
a) Manufacturer's name or trademark
b) Manufacturer's type
c) Manufacturer's serial number (SER), numerals only
d) Rated voltage (PRI)
e) Ratio or ratios
f) Basic impulse insulation level (BIL kV)
g) Rated frequency (in Hertz)
h) Thermal burden rating or ratings at ambient temperature or temperatures, in voltamperes in degrees Celsius
i) Accuracy rating: maximum standard burden at which the accuracy rating is 0.3 class, as a minimum.
Terminals
Primary terminals shall be electrically and mechanically suitable for use with either copper or aluminum conductors. Secondary terminals shall be electrically and mechanically suitable for use with copper conductors.
What is a Voltage Transformer with respect to C57.13?
Terms in which ratings shall be expressed
The ratings of a voltage transformer shall include:
a) Basic impulse insulation level in terms of full-wave test voltage
b) Rated primary voltage and ratio
c) Frequency (in Hertz)
d) Accuracy ratings
e) Thermal burden rating
Standard burdens
Standard burdens for voltage transformers for rating purposes are shown in table below.
Assignment of accuracy ratings
A voltage transformer shall be assigned an accuracy rating for each of the standard burdens for which it is rated. For example, an accuracy rating might be 0.3W and X, 0.6Y, 1.2Z.Accuracy classification for voltage transformers with two secondary windings or tappedsecondary windings - The burden on any two secondary terminals affects the accuracy on all other terminals. The burden stated in the accuracy ratings is the total burden on the transformer. The accuracy class shall apply with the burden divided betweenthe secondary outputs in any manner.
Thermal burden ratings
The thermal burden rating of a voltage transformer shall be specified in terms of the maximum burden in voltamperes that the transformer can carry at rated secondary voltage without exceeding the temperature rise. If no thermal burden in voltamperes rating is given, the thermal burden rating in voltamperes shall be the same as the maximum standard burden for which an accuracy rating is given.
Each winding, including the primary winding, of a multiple-secondary transformer shall be given a thermal burden rating. If only one thermal burden rating is specified, it shall be applicable to any distribution of secondary voltamperes, including the use of taps.
Nameplates
Voltage transformers shall be provided with nameplates that shall include, as a minimum, the following information:a) Manufacturer's name or trademark
b) Manufacturer's type
c) Manufacturer's serial number (SER), numerals only
d) Rated voltage (PRI)
e) Ratio or ratios
f) Basic impulse insulation level (BIL kV)
g) Rated frequency (in Hertz)
h) Thermal burden rating or ratings at ambient temperature or temperatures, in voltamperes in degrees Celsius
i) Accuracy rating: maximum standard burden at which the accuracy rating is 0.3 class, as a minimum.
Primary terminals shall be electrically and mechanically suitable for use with either copper or aluminum conductors. Secondary terminals shall be electrically and mechanically suitable for use with copper conductors.
Comments
Post a Comment