TYPES OF FUSES FOR ELECTRIC MOTORS PROTECTION
Different types of fuses for electric motor protection
Different types of fuses for electric motor protection
Fuses are over-current protective devices that are placed in an electrical circuit to protect the control components, wiring, insulation, and motor from damage caused by excessive current and associated heat. Overcurrents are considered any increase in continuous current above the normal operating current level. In motor circuits, overcurrents are classified in two different categories. Motor overloads are any overcurrents up to or slightly above locked rotor current (6-8 times FLA).
This range of overcurrent is protected by overload relay protection devices which will be discussed in more detail later. Short-circuit overcurrents are those produced by short-circuit or ground fault conditions with fault current levels in excess of 8 times FLA.
In today’s industrial facilities, short-circuit overcurrents can easily reach 50,000A. If the short-circuit overcurrents are not interrupted within fractions of a second, severe damage to the electrical installation can occur including motor damage, conductor and controller damage or even fires.
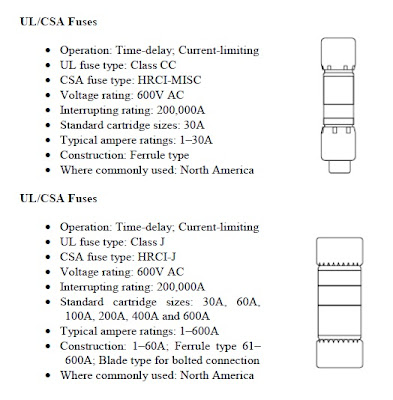
In motor circuits, fuses best provide protection from damage caused by short–circuit currents. Throughout the world, many different types of fuses are used for shortcircuit protection in motor circuits. In North America, UL and CSA fuses are most commonly used. In other parts of the world, DIN (German) and BS88 (British) fuses are dominant. Even though the construction and fastening means are quite different (See different types of fuses below), all these fuses still perform the same essential function of short-circuit protection.
Different Types of Fuses



Very informative post. Keep it up. transmission lines design
ReplyDelete